Need Appointment ?
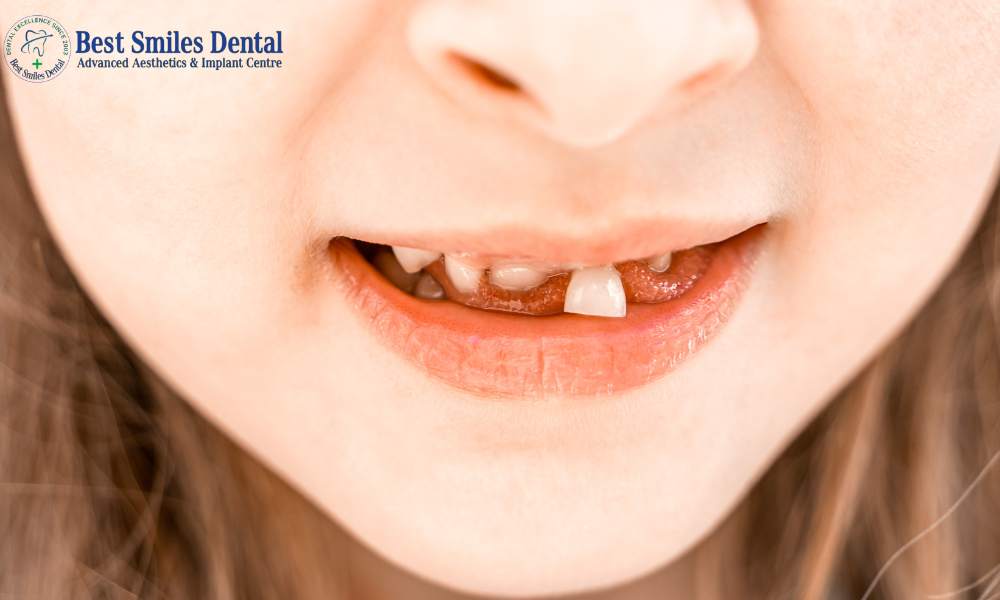
Decayed Milk Teeth Treatment
Decayed milk teeth in children (or cavities) is caused by bacteria in the mouth damaging the teeth. This bacteria is called plaque. It attaches itself to the tooth’s enamel and ultimately damages enamel as it eats away at the protective covering.
Book Appointment to find out which treatment might be best for your kids at Best Smiles Advanced Dental Clinic.
Which children are at risk for Tooth Decay?
All children are at risk for tooth decay if proper precautions are not taken. Children with poor oral hygiene are more likely to struggle with tooth decay. It’s important to practice good oral habits with your children such as routine tooth brushing and flossing and scheduling regular visits to the dentist.
Kids with the following risk factors are more likely to grapple with tooth decay:
- Those with lots of bacteria, which can cause cavities.
- Children who eat too many sugars and carbohydrates.
- Kids who do not have fluoride in their available water supply;
- Kids who experience dry mouth.
- Those with deep grooves in their teeth, especially molars’
- Children who sleep with a bottle.
What are the common treatments for decayed milk teeth?
Treatment options for decayed milk teeth depend greatly on the stage at which the decay is discovered and dealt with. The following treatments are all options for tooth decay in children:
- Fluoride treatment – When decay is found at an early stage, remineralization with fluoride can treat and reverse decay.
- Dental filling – If decay reaches a stage where it is irreversible, the child needs a dental filling to stop the cavity-forming from getting worse.
- Pulpectomy – When the cavity is large and the pulp of the tooth is infected or exposed, your child needs to have the infected or damaged pulp removed followed by a filling or crown.
- Crown – If the damaged area is too large to be treated with a filling, your dentist may recommend a crown to cover the exposed hole.
- Antibiotics – If an abscess forms, your child may need antibiotics to treat their infection.
- Extraction – Sometimes extracting the damaged tooth is a good option. Usually, this is done when a primary tooth (also known as a baby tooth) would have been lost soon.
How decayed milk teeth be prevented?
We all agree that decayed milk teeth should be avoided, but how? Here are some practical steps you can take to prevent tooth decay in children:
- Teach children to practice good oral hygiene at an early age. Help them to develop healthy habits like brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily. Teach them how much toothpaste to use, how long to brush, and to be sure to brush back teeth well.
- Ensure your child is getting enough fluoride. While fluoride is present in bottled water and many city water sources, its levels are low. Children should use a toothpaste with fluoride and get fluoride polish treatments during routine cleanings at their dentist’s office. If your water is not fluoridated, your dentist or pediatrician can provide supplements.
- You may also choose to limit your child’s access to certain foods. Foods high in sugar, juices, and candy can damage tooth enamel and cause cavities. If you approve of these foods, consider having your child rinse their mouth or brush their teeth after eating.

Pain-Free Dentistry
Comfortable, stress-free treatments every time.

Next-Gen Equipments
Precision care with advanced technology.

Expert Care Guaranteed
Trusted specialists for superior oral health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Discover everything you need to know about professional tooth cleaning and polishing. Learn how it removes plaque, enhances your smile, and promotes better oral health.
Yes, treating decayed milk teeth is very essential. They help in chewing, speaking, and maintaining space for permanent teeth. Untreated decayed teeth can cause pain, infection, and affect the health of developing permanent teeth.
- White or brown spots on teeth
- Tooth sensitivity or pain
- Swelling or redness in the gums
- Visible cavities or holes in the teeth
Q3: How is decay in milk teeth treated?
Treatment depends on the severity of the decayed milk teeth:
- Fluoride treatments for early-stage decay
- Fillings to restore the tooth
- Pulp therapy for deep decay affecting the tooth's nerve
- Extractions if the tooth cannot be saved
No, pediatric dentists use local anesthesia and child-friendly techniques to ensure the procedures are pain-free and comfortable for children.
Yes, if decay spreads to the roots, it can damage the developing permanent teeth beneath. It can also lead to infections and alignment issues if the decayed tooth falls out prematurely.
The cost varies depending on the extent of decay, type of treatment, and the clinic. Pediatric dental procedures are usually affordable and customized to suit the child’s needs.

